Accuracy in BrainTrawler¶
Preprocessing¶
BrainTrawler is designed as an exploratory tool. To ensure fast computations, the accuracy of the data is a bit reduced: For region-level datasets we have double precision (floats with 64 bits). For voxel-level datasets we have transformed the values to integers with values between 1-255. So the range is scaled to this space and any decimal places are cut off. For the dataset specific preprocessing have a look at the Browse Database page. For further information ask the person responsible for data ingestion.
Comparison with Allen Brain¶
The Hawrylycz 2012 dataset is the Allen Human Brain dataset also used on https://human.brain-map.org/ . The preprocessing of this dataset in BrainTrawler follows the publication Arnatkevic̆iūtė et al, 2019 where the expression values are harmonized over the six donor brains. So the expression-level of each sample normalized by the scaled robust sigmoid normalization to be between 0 and 1 (range between minimum and maximum), so that they are comparable between the 6 donors. Furthermore, they are aggregated. This means, there is then only one value per gene - in contrast to Allen Brain.
Now let’s compare the results in BrainTrawler and from the Allen Brain page https://human.brain-map.org/ :
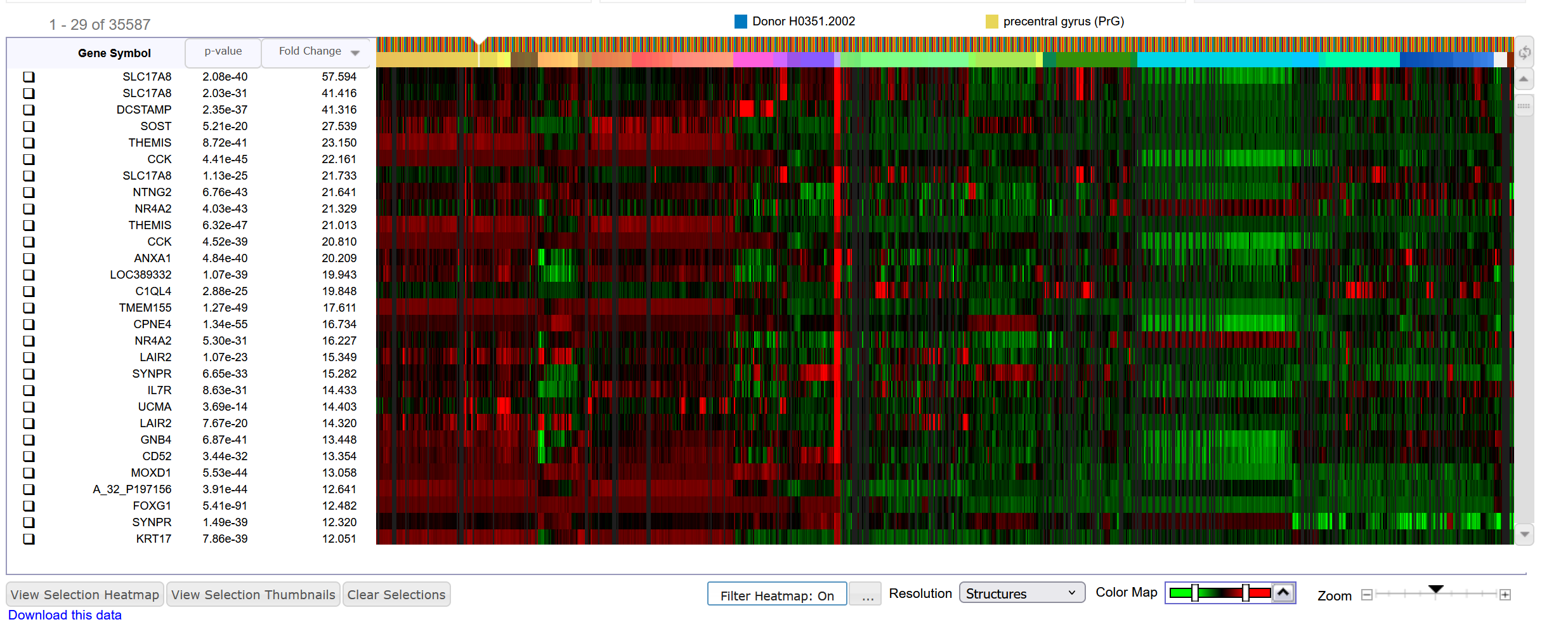
On the Allen Brain page https://human.brain-map.org/ do a differential search with regions left and right Claustrum as target structures and the brain as contrast structure. You get this result:
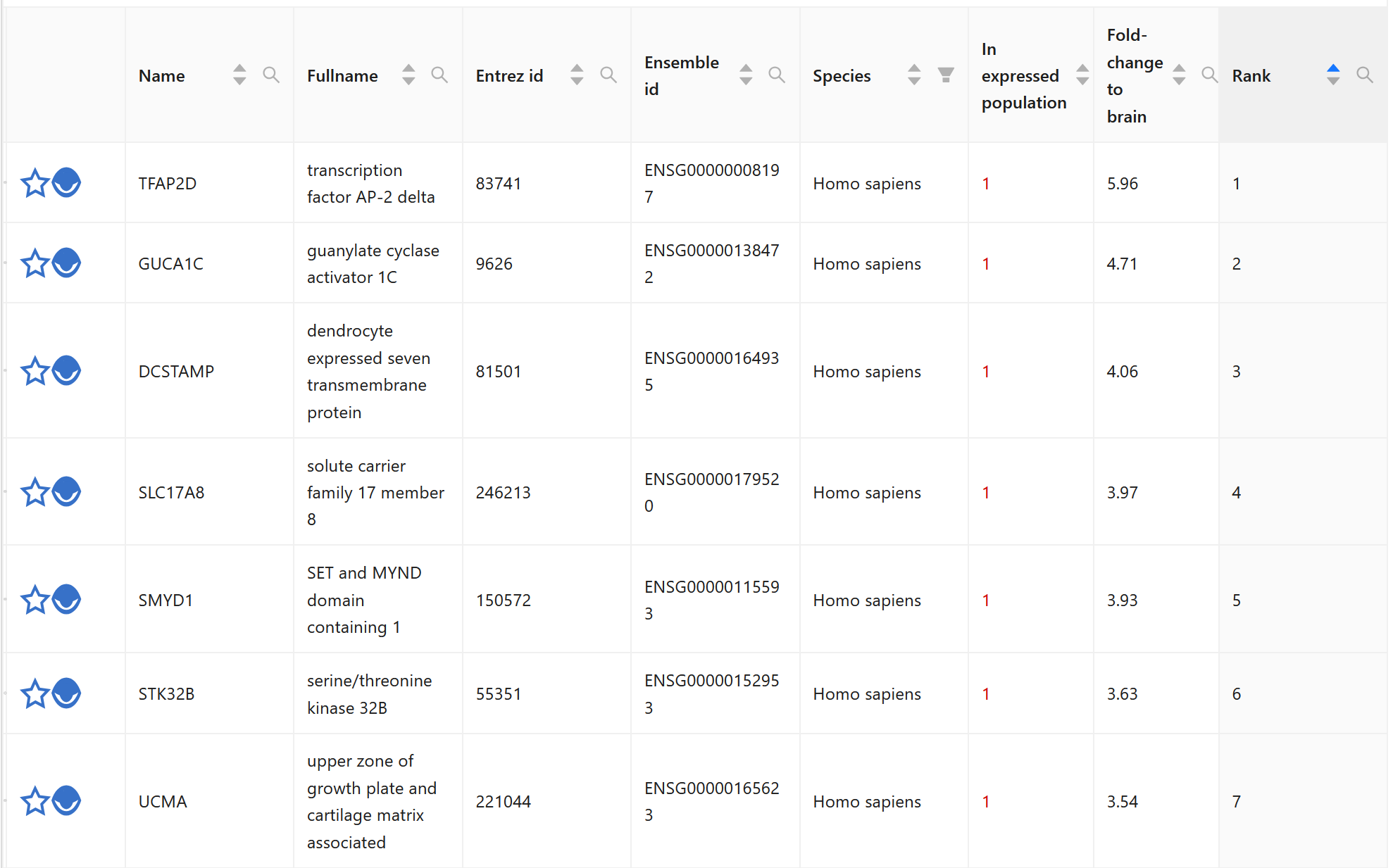
In BrainTrawler, human version, do a gene expression query with left and right Claustrum, dataset Hawrylycz 2012 and do a region-specificity query (fold-change to brain). You get this result:
So the results are different:
Allen Brain has multiple probes per gene
The magnitude of the fold-changes is different
The order of the genes is different,
The reasons for this are the following:
In BrainTrawler the gene expression values are aggregated - so there is only one value per gene.
In the Allen Brain page the fold change is defined by 2^(average(R1)-average(R2)) with R1, R2 being the log2 values of the samples, see https://community.brain-map.org/t/transcriptomics-rna-seq-microarray-data-normalization-faq/182/6 . In contrast to that, in BrainTrawler we divide the normalized gene expression of R1 by the normalized gene expression of R2. Therefore, the magnitude of the fold changes from Allen Brain are so much higher.
The order of the genes is different because of the different values that are used: log2 values, multiple values in Allen Brain vs. aggregation and normalization in BrainTrawler.
DGEA t-tests¶
The Differential Gene Expression Analysis (DGEA) in BrainTrawler is on t-tests with FDR correction (Benjamini-Hochberg procedure). These t-tests require a normal distribution of gene expression values. This assumption might not always be fulfilled. Therefore, this feature should only be used for hypothesis generation and results obtained here should be validated further.
